Solutions
Concept:
- Resistance is the ability of any electrical component to resist electric current across it.
- Equivalent Resistance can be defined as the resistance of the resistor which will replace all the resistors between two points and will draw the same current between these two points as it was flowing Earlier.
- Ohms Law: At constant temperature, a potential difference is the product of current and resistance.
Series and Parallel Connection:
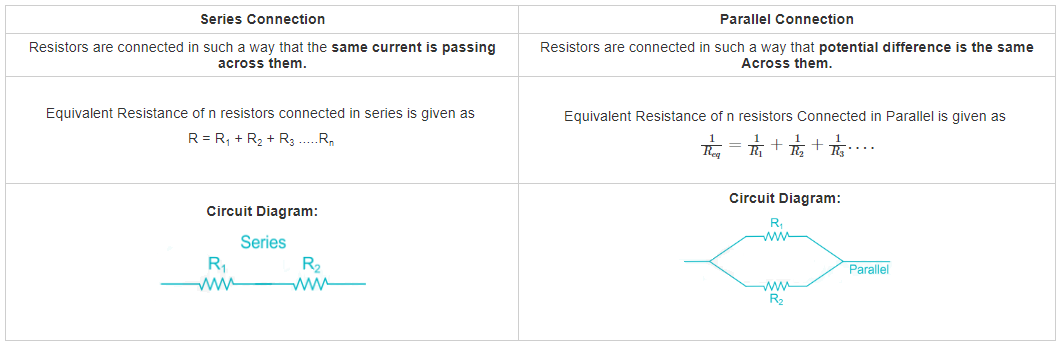
Calculation:
Here in the diagram, three resistors are present.
We have to find resistances between A and B.
From A to B, we have two paths, 1 is direct having resistance 40 Ω.
The second is via C, where 100 Ω and 60 Ω resistors are in series.
Equivalent resistance across A the bath of ACB will be sum of these two resistors as they are in series.
So, Resistance R ACB = 60 Ω + 100 Ω = 160 Ω
Also, this combination is in Parallel with 40 Ω resistor.
The equivalent resistance is
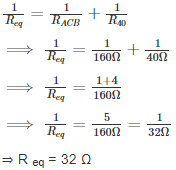
⇒ R eq = 32 Ω
So, the correct option is 32 Ω.



 Get latest Exam Updates
Get latest Exam Updates 





 ×
×






